Tier2Assist¶
The basic premise of the design is that after we submit the ticket to your PSA, we give you access to the information and allow you to suggest additional steps to the user.
These suggestions are made through series of if statements which use Python syntax. The commands you write are literally interpreted by Python 3 on the users computer, so you have a full fledged programming language at your disposal to make your rules.
NOTE: Some browsers require url encoded strings to function so if you have issues with things like quotes, spaces, or slashes in your urls, replace them with the url encoded replacement. https://www.w3schools.com/tags/ref_urlencode.ASP
Edit Tier2Assist¶
There are two views for these rules:
Visual Editor¶
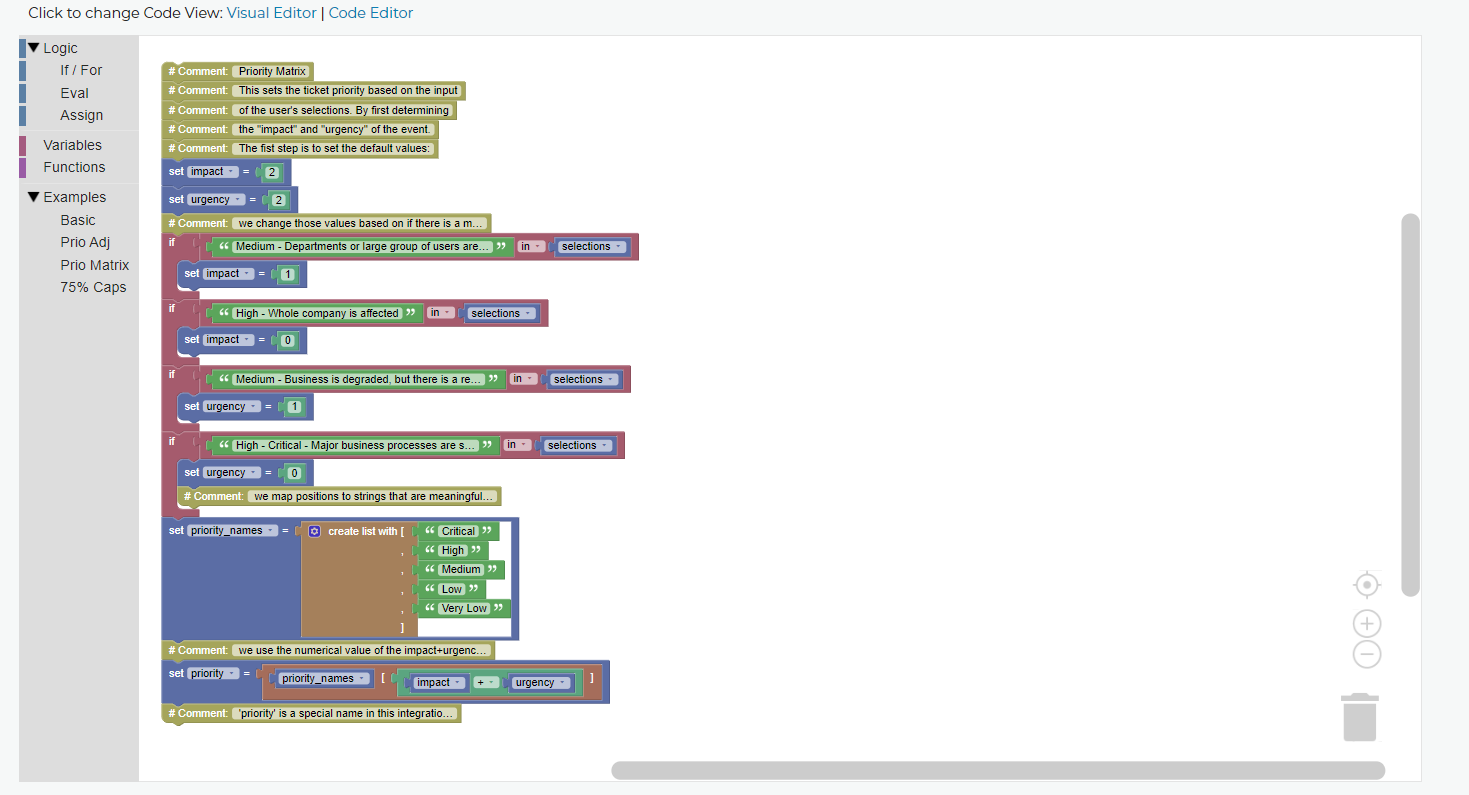
The Visual Editor has several features to make dealing with code a bit more friendly. The most useful functions and variables are already populated and there is example code to play with by dragging and dropping onto the sandbox area. Pieces snap together to make sure the code works properly, and most of the variables and functions can be right-clicked for help about what they are and how they work.
Code Editor¶
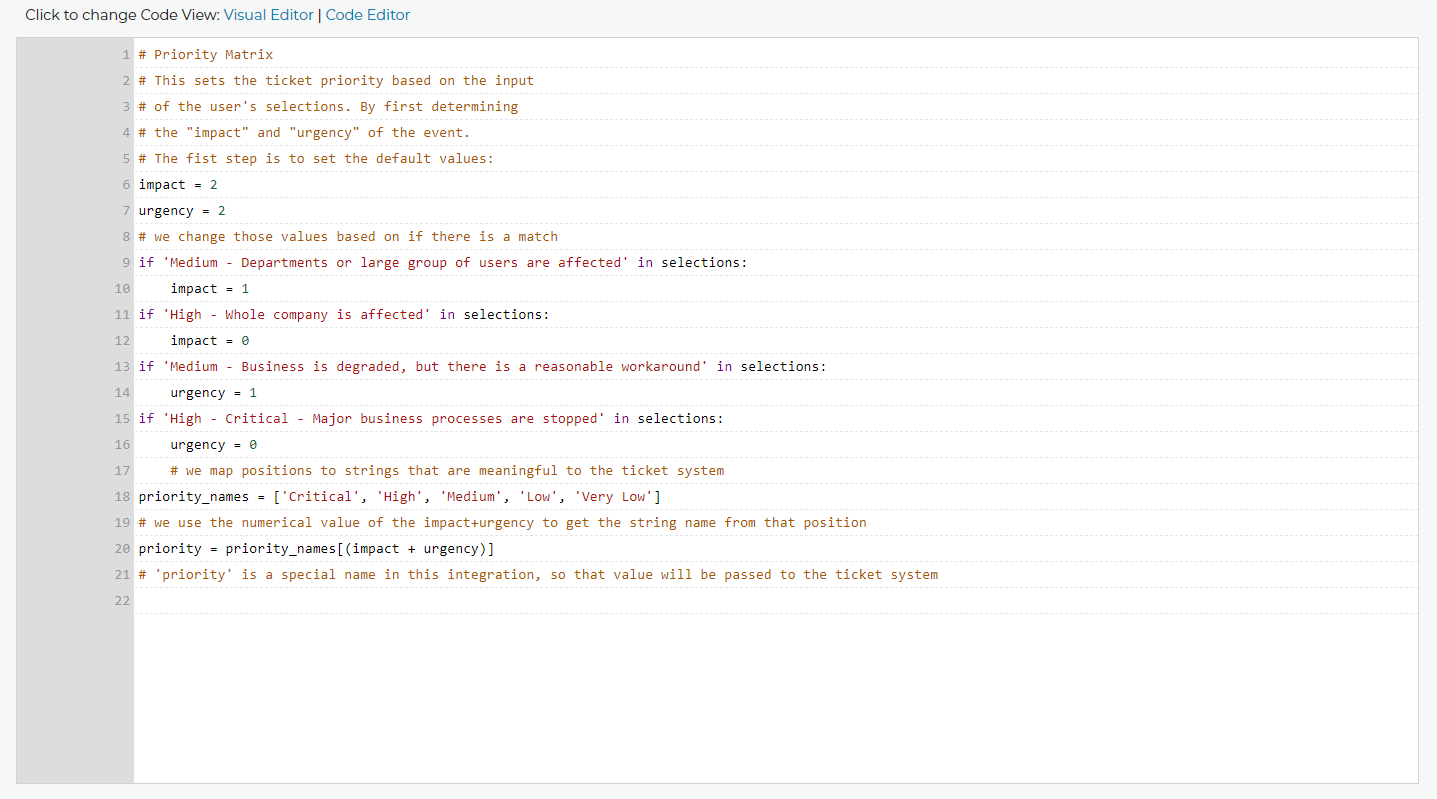
The Code Editor assumes you know what you are doing so all you see is the code and the line numbers.
Test Rules¶
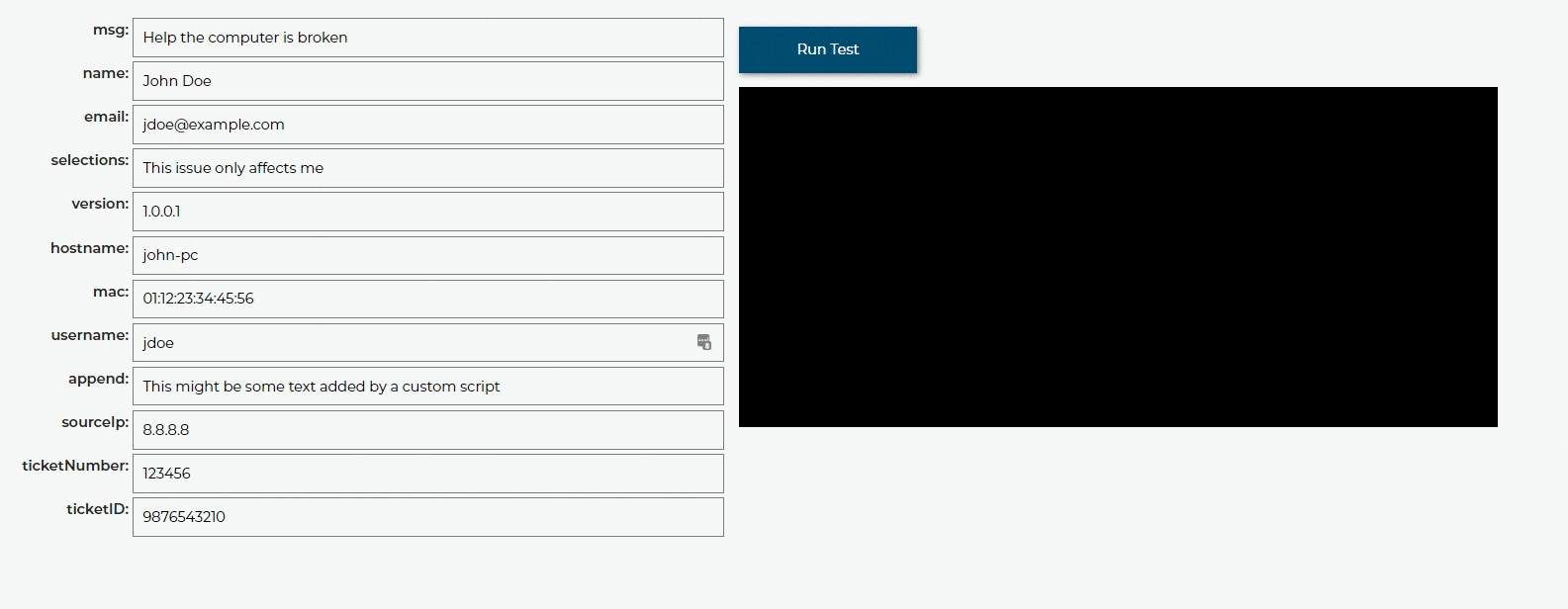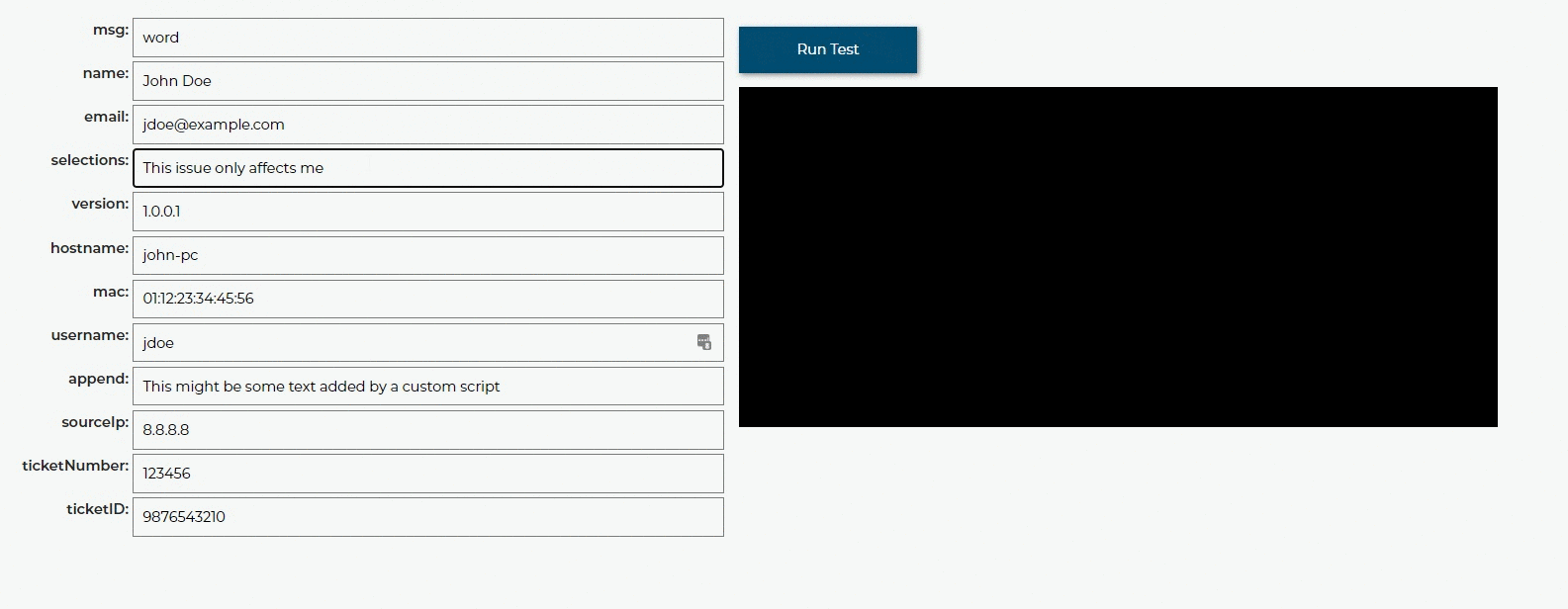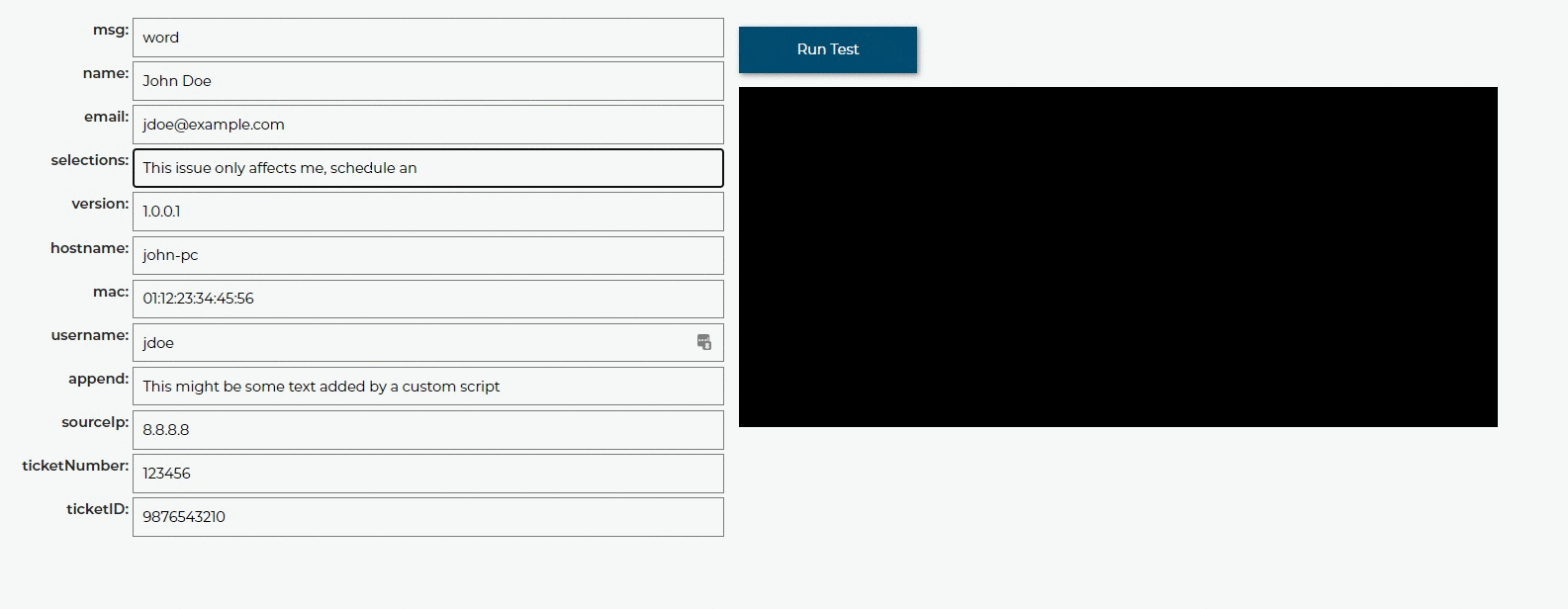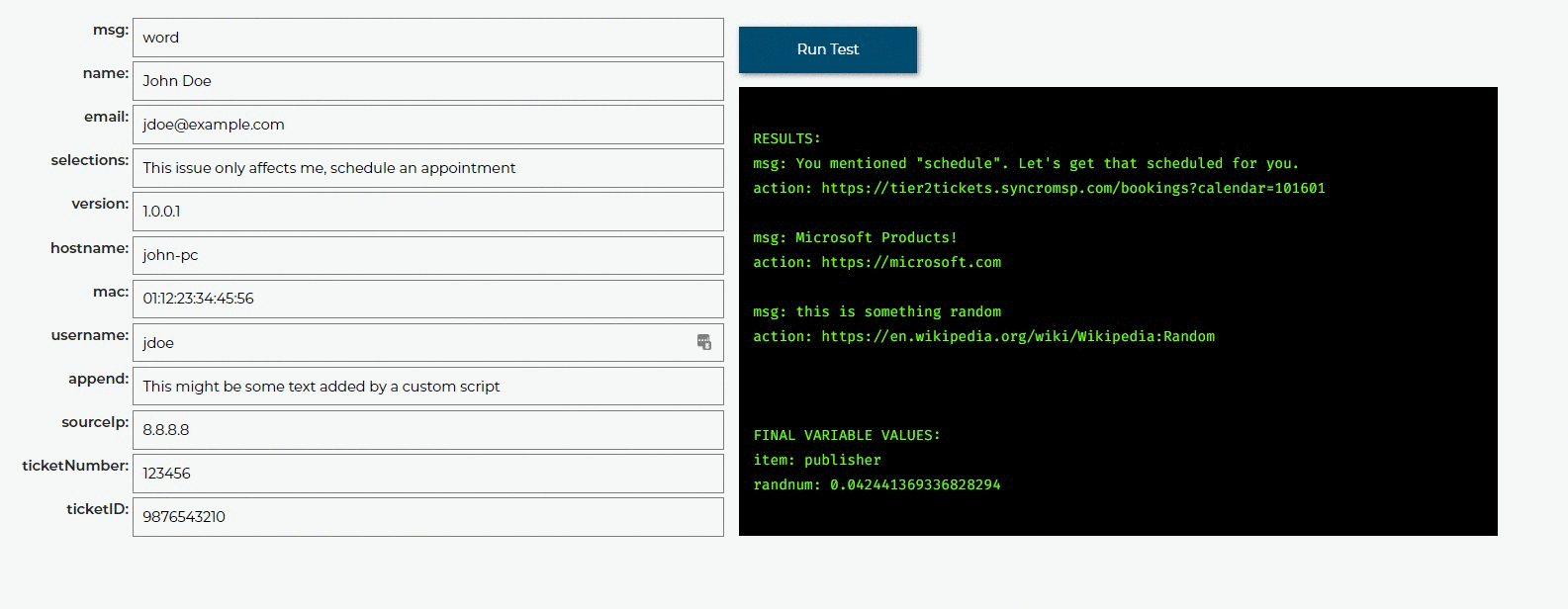
You can also test these rules by inputting test data and running the rules against that data. All variables will be outputted so you can see how the rules change them. If there is a syntax error in the rules we will let you know where, you can also click the link to see the error in the Code Editor.
The test shows everything in a raw format for people who want to know everything about what is happening. You don’t have to worry about things like repeating identical actions appearing on the clients side.
Save Rules¶
Make sure to save the changes to your rules! The code will be tested to make sure there are no syntax errors, and you will get a message letting you know if it was successful. Once you save your rules they will be implemented immediately for every endpoint connected to your account with an internet connection. The next time a user starts the software these rules will apply. There is no need to rebuild the software.
Variables¶
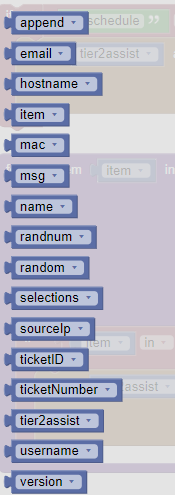
The first thing you need to know when writing a rule is which variables you have available to you. These variables are fixed and should be available to any integration.
You can see the variables available in the Visual Editor of the Tier2Assist but here they are for reference. For more information take a look at the A deeper dive into Variables section below
Special Functions¶
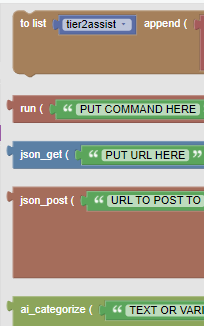
The majority of the functions provided are built into python, but there are a few special functions we wrote that might be useful to you for building out your Tier2Assist Rules.
You can see this list in the Visual Editor of the Tier2Assist but here they are for reference. For more information take a look at the A deeper dive into Functions section below
What the user sees¶
This is what the user will see after submitting a ticket, if the rules determine a Tier2Assist should be shown.
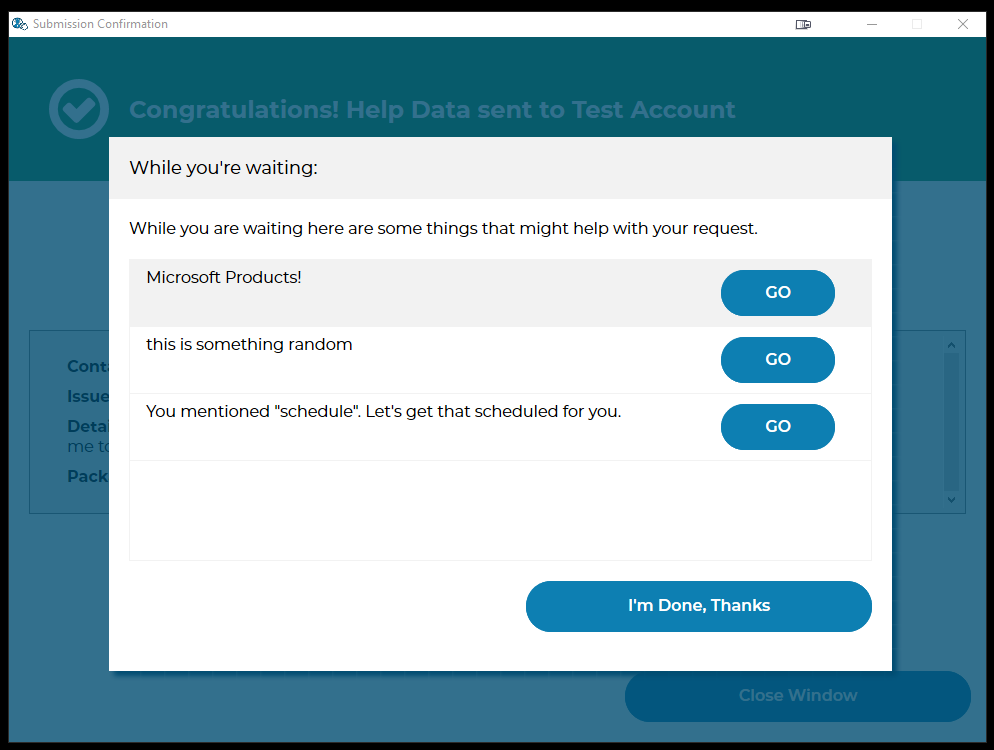
A Tier2assist consists of a message (the text that shows up beside the button) and an action (the command run on the users machine if they click the button).
Examples¶
To show how powerful this can be and give you an idea of how to use it, we came up with a few example rules here:
Running Tier2Assists before ticket submission¶
The variable “is_before_ticket_submit” allows you to schedule Tier2Assists before or after ticket submission. The variable is true when before the submission and false after. The default behavior is to always run after the ticket submission. If you want to do somethings before ticket submission and others after you will need to use this variable to separate your code
if is_before_ticket_submit:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'THIS TIER2ASSIST WILL SHOW UP BEFORE THE TICKET IS SUBMITTED', 'action': 'https://www.google.com/search?q=before'})
if not is_before_ticket_submit:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'THIS TIER2ASSIST WILL SHOW UP AFTER THE TICKET IS SUBMITTED', 'action': 'https://www.google.com/search?q=after'})
Chat¶
First off, “selections” is the text that makes up which radio buttons and checkboxes were selected by the user in the GUI. So let’s assume you have a checkbox that says “Chat with us” and you want that check box to cause an option to open a direct chat via tawk.to. This is what that rule would look like:
if 'chat' in selections:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'You mentioned "chat". We can chat with you right now!', 'action': 'https://tawk.to/chat/5e9ef98435bcbb0c9ab343d5/default'})
Reboot¶
As another example, let’s assume you want to always show an option for the user to reboot thier machine. Here is what that rule would look like:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Sometimes a reboot alone will resolve issues, would you like to reboot now?', 'action': 'cmd /c title Preparing to reboot...^&color 4f^&echo. ^&echo Preparing to reboot. To cancel, close this window.^&ping -n 9 127.0.0.1^>nul^&shutdown -r -f -t 0'})
Google Forms¶
Now let’s say you have a form that needs to be filled out upon new employees being hired. If you want to show an option to fill out this form based on the keywords hiring, hire, and new employee appearing in the message, here is what that rule might look like:
for phrase in ['hiring', 'hire', 'new employee']:
if phrase in msg.lower():
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'If you are looking to add a new employee please fill out this form.', 'action': 'YOUR_FORM_URL_HERE' + ticketID})
You can now use Tier2AI to perform the same thing without having to list keywords to match against
categories = ['new hire']
result = ai_categorize(msg, categories)
if result['best_match'] == 'new hire':
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'If you are looking to add a new employee please fill out this form.', 'action': 'YOUR_FORM_URL_HERE' + ticketID})
Additionally we have some special integrations with google forms Tier2Forms to allow the information from a submission of such a form to the ticket that was just created.
Cognito Forms¶
Now let’s say you have a form that needs to be filled out upon new employees being hired. This example uses Tier2AI
categories = ['new hire']
result = ai_categorize(msg, categories)
if result['best_match'] == 'new hire':
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'If you are looking to add a new employee please fill out this form.', 'action': (('https://www.cognitoforms.com/Tier2Technologies1/SimpleForm' + '?entry={"TicketID":') + ticketID) + '"}'})
Additionally we have some special integrations with Cognito forms Tier2Forms to allow the information from a submission of such a form to the ticket that was just created.
Password Reset¶
If you wanted to show a password reset link if both office and password were included in the ticket message, a rule like this may be appropriate:
if 'password' in msg and 'office' in msg:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Click here to reset your office password.', 'action': 'https://account.live.com/password/reset'})
If you wanted to show a password reset link if either office or password were included in the ticket message, a rule like this may be appropriate:
if 'password' in msg or 'office' in msg:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Click here to reset your office password.', 'action': 'https://account.live.com/password/reset'})
Schedule an appointment¶
Now let’s say you want to allow a user to schedule an appointment. Here is a rule that does this if they select a checkbox that contains the word schedule:
if 'schedule' in selections:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'You mentioned "schedule". Let\'s get that scheduled for you.', 'action': 'https://tier2tickets.syncromsp.com/bookings?calendar=101601'})
External API: Example Activity¶
We also allow connecting to external APIs. This is a fun API that suggests activities if someone is bored. It is an open API that does not require an API KEY
activity = json_get('https://www.boredapi.com/api/activity')
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Activity of the day: ' + activity['activity'], 'action': 'https://google.com/search?q=' + activity['activity']})
External API: Example Slack (Using Slack APPS)¶
This method requires that you have set up an app in slack with an Incoming Webhook, a bot, and give the bot permissions to post in the channel
postURL = 'PUT_WEBHOOK_URL_HERE'
post_result = json_post(postURL, {'text': 'New ticket created. Ticket number: ' + ticketNumber})
Random¶
Sometimes it is best to have an option show up randomly (Customer Satisfaction surveys for instance). This rule will show up randomly (around 50% of the time) to give the user a random Wikipedia article:
if random.random() <= 0.5:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'this is something random', 'action': 'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Random'})
Survey¶
What if you wanted to get feedback from your users about your service? You could use a simple form (Cognito in this case)
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'How has your experience been with us? We would like to know more with this simple 1 question survey', 'action': "https://www.cognitoforms.com/Tier2Tech/HelpDeskButtons?entry={%22Name%22:%22"+name+"%22,%22Email%22:%22"+email+"%22}"})
Time Based Actions¶
What if you wanted to send users to a link during business or after hours.
import datetime
#start and end times should be given in 24 hour format
start = datetime.time(17,0) #1700 is 5:00 PM
end = datetime.time(7,50) #0750 is 7:50 AM
timenow = datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone.utc).time()
#start time and end time are optional. they are only used to create the text demonstrating how the assist works.
starttime = start.strftime("%H:%M %p")
endtime = end.strftime("%H:%M %p")
def in_between(now, start, end):
if start <= end:
return start <= now < end
else:
return start <= now or now < end
#remember to change the msg and action of the assist
if in_between(timenow, start, end):
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Please note the time is between {starttime} and {endtime}!'.format(starttime=starttime, endtime=endtime), 'action': 'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Random'})
Big Example¶
Each of the previous examples should be viewable in the Visual Editor, but if you would rather, you can copy and paste this set of examples directly into the code editor and start playing around.
categories = ["new hire", "broken computer"]
result = ai_categorize(msg, categories)
#anything listed under here will only happen before the ticket submission process
if is_before_ticket_submit:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'THIS TIER2ASSIST WILL SHOW UP BEFORE THE TICKET IS SUBMITTED', 'action': 'https://www.google.com/search?q=before'})
#this will show a random article on wikipedia 50% of the time
if random.random() <= 0.5:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'this is something random', 'action': 'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Random'})
#this will ask the user to click a button to reboot the machine
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Sometimes a reboot alone will resolve issues, would you like to reboot now?', 'action': 'cmd /c title Preparing to reboot...^&color 4f^&echo. ^&echo Preparing to reboot. To cancel, close this window.^&ping -n 9 127.0.0.1^>nul^&shutdown -r -f -t 0'})
#this will prompt the user to open a google search if the AI is more than 94% sure the message is about a broken computer
if result['scores']['broken computer'] >94:
tier2assist.append({'msg':'It looks like you are having a computer problem...', 'action':'http://google.com/search?q=how+to+fix+computer'})
#anything listed under here will only happen after the ticket submission process
if not is_before_ticket_submit:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'THIS TIER2ASSIST WILL SHOW UP AFTER THE TICKET IS SUBMITTED', 'action': 'https://www.google.com/search?q=after'})
#this will pull an activity from the boredapi and show the results for it in a google search
activity = json_get('https://www.boredapi.com/api/activity')
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'Activity of the day: ' + activity['activity'], 'action': 'https://google.com/search?q=' + activity['activity']})
#this will prompt the user to schedule an appointment, if they click on anything that has the word schedule in it
if 'schedule' in selections:
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'You mentioned "schedule". Let\'s get that scheduled for you.', 'action': 'https://tier2tickets.syncromsp.com/bookings?calendar=101601'})
#this will prompt the user to fill out a form if the AI thinks the message is about a new hire and add the responses from the form to the ticket notes
if result['best_match'] == 'new hire':
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'If you are looking to add a new employee please fill out this form.', 'action': (('https://www.cognitoforms.com/Tier2Technologies1/SimpleForm' + '?entry={"TicketID":"') + ticketID) + '"}'})
Create Actions Based on Email Domain¶
If you’d like to create actions based on the email address your customer used, copy and paste the following examples:
#for a list of domains to perform the same action
#create list
domain_list = ['example.com', 'example.org', 'example.net', 'example.io']
for domain_item in domain_list:
if domain_item in email.lower():
# add if action here i.e queue, technician, type/subtype, example on next line
# queue = ‘match-all-characters-even-spaces’
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'It sounds like Example_Domain has hired a new teammate! Click “Go” to fill out the new employee form.', 'action': 'Google Tier2Form Link' + ticketID})
#For a single domain to do a single thing
if 'example.xyz' in email.lower():
# add if action here i.e queue, technician, type/subtype, example on next line
# queue = ‘match-all-characters-even-spaces’
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'It sounds like Example.xyz has hired a new teammate! Click “Go” to fill out the new employee form.', 'action': 'Google Tier2Form Link' + ticketID})
A deeper dive into Functions¶
There are a few special functions written by our team to provide additional functionality within Tier2Assist Rules.
tier2assist.append¶
tier2assist.append({'msg': 'ADD TIER2ASSIST MESSAGE HERE', 'action': 'ADD ACTION HERE'})
This is a really important one. It allows you to add A Tier2Assist. Combine this with if statements to show only the assists the end user may find helpful.
run¶
run('PUT COMMAND HERE')
This function allows you to run a command on the users machine. It works similarly to the RUN command in windows.
json_get¶
json_get('PUT URL HERE')
This function allows you to access and external API or website using a GET.
json_post¶
json_post('URL TO POST TO', {'FIELD NAME 1': 'DATA FOR FIELD NAME 1', 'FIELD NAME 2': 'DATA FOR FIELD NAME 2', 'FIELD NAME 3': 'DATA FOR FIELD NAME 3'}, {'HEADER TAG1': 'HEADER DATA1'})
This function allows you to access and external API or website using a POST. The headers are optional.
A deeper dive into Variables¶
When designing these custom rules, there are certain variables which will always be available to you because they correspond with input from our application and not from the ticket system integration being used. They are outlined as follows.
name¶
The end-user’s name. This may be the name they entered into the input field or what the ticket system says is the name for that email address:
append¶
Refers to some text that has been appended to the message. This typically will have been generated by a Tier2Script :
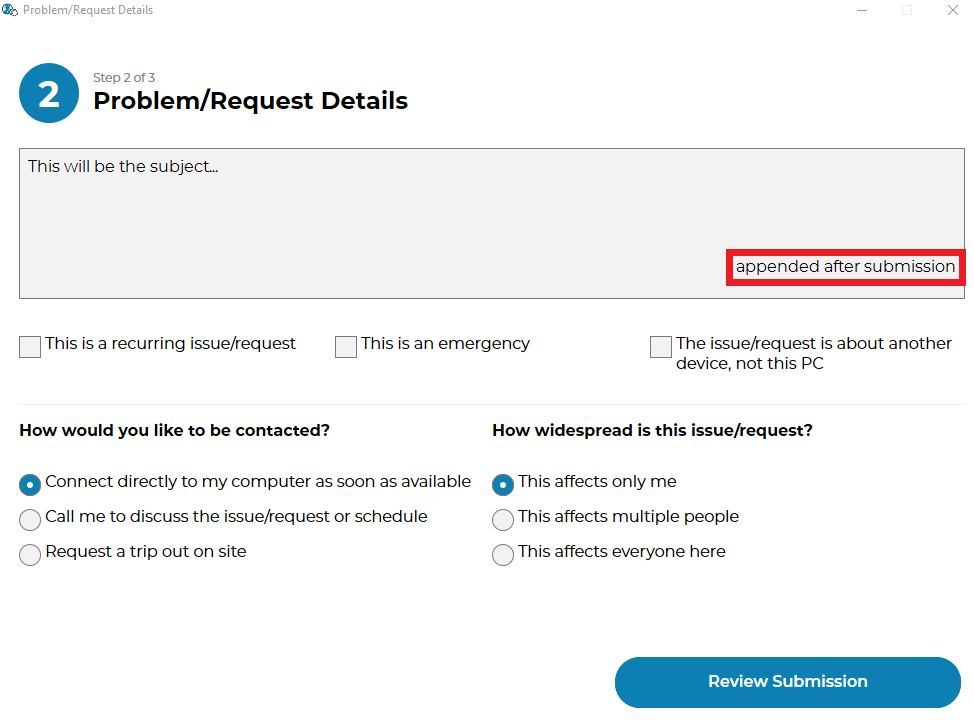
ticketID¶
The internal ticket ID the PSA uses to identify each ticket (often different from the ticket number)
ticketNumber¶
The ticket number the user will most likely see to identify a ticket (often different from the ticket id)
username¶
The username of the windows account that submitted the current ticket.
version¶
The version number of the HDB software